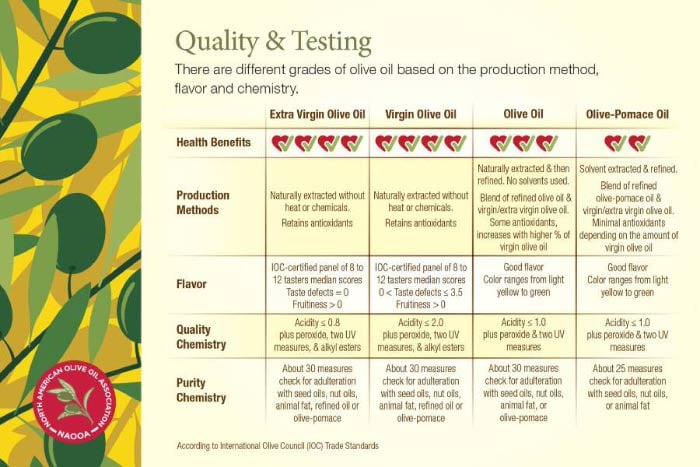
When comparing extra virgin olive oil vs virgin olive oil, the key differences come down to quality standards, flavor, and free acidity levels. Both are natural olive oils made without chemicals or heat, but extra virgin olive oil meets stricter requirements.
How Olive Oil Is Classified
Olive oils are graded according to standards set by the International Olive Oil Council (IOC), a United Nations–recognized organization that has served as the global authority on olive oil quality for more than 50 years.
Under these standards, both extra virgin and virgin olive oils must be:
-
Extracted only by mechanical means
-
Produced without heat or chemical solvents
-
Evaluated using chemical analysis and sensory (taste) testing
Once extracted, the oil is graded based on acidity and sensory quality.
What Is Extra Virgin Olive Oil?
Extra virgin olive oil is the highest quality grade of olive oil.
To qualify as extra virgin, the oil must:
-
Be free of sensory defects
-
Exhibit positive fruity characteristics
-
Have a free acidity of 0.8% or lower
Extra virgin olive oil is prized for its freshness, flavor, and versatility, making it suitable for finishing dishes, salad dressings, and everyday cooking.
What Is Virgin Olive Oil?
Virgin olive oil is also mechanically extracted and unrefined, but it allows for minor sensory defects.
Virgin olive oil must:
-
Show slight flavor or aroma imperfections
-
Have a free acidity between 0.8% and 2.0%
While still a natural olive oil, virgin olive oil does not meet the stricter quality threshold required for extra virgin classification.
Extra Virgin Olive Oil vs Virgin Olive Oil: Key Differences
| Feature | Extra Virgin Olive Oil | Virgin Olive Oil |
|---|---|---|
| Extraction method | Mechanical only | Mechanical only |
| Sensory defects | None allowed | Minor defects allowed |
| Free acidity | ≤ 0.8% | 0.8%–2.0% |
| Quality grade | Highest | Lower than extra virgin |
| Retail availability (U.S.) | Widely sold | Rarely sold |
Antioxidants and Polyphenols: What to Know
Both extra virgin and virgin olive oils naturally contain antioxidants and polyphenols, compounds linked to olive oil’s health benefits.
However, polyphenol levels vary independently of grade:
-
A mild-tasting extra virgin olive oil may contain fewer polyphenols
-
A robust-tasting virgin olive oil may contain more
Factors such as olive variety, harvest timing, freshness, and flavor intensity all influence polyphenol content.
Why Virgin Olive Oil Is Hard to Find in Stores
In North America, virgin olive oil is rarely sold at retail. Most consumers encounter either:
-
Extra virgin olive oil, or
-
Refined olive oil blends labeled simply as “olive oil”
As a result, the distinction between extra virgin and virgin olive oil is often unfamiliar to consumers—even though both are defined by international standards.
Learn More About Olive Oil Grades
For a deeper explanation of olive oil classifications and quality standards, download our guide to olive oil standards (PDF) or watch our educational video on olive oil grading.
For more information on olive oil grading and standards, watch the video below.